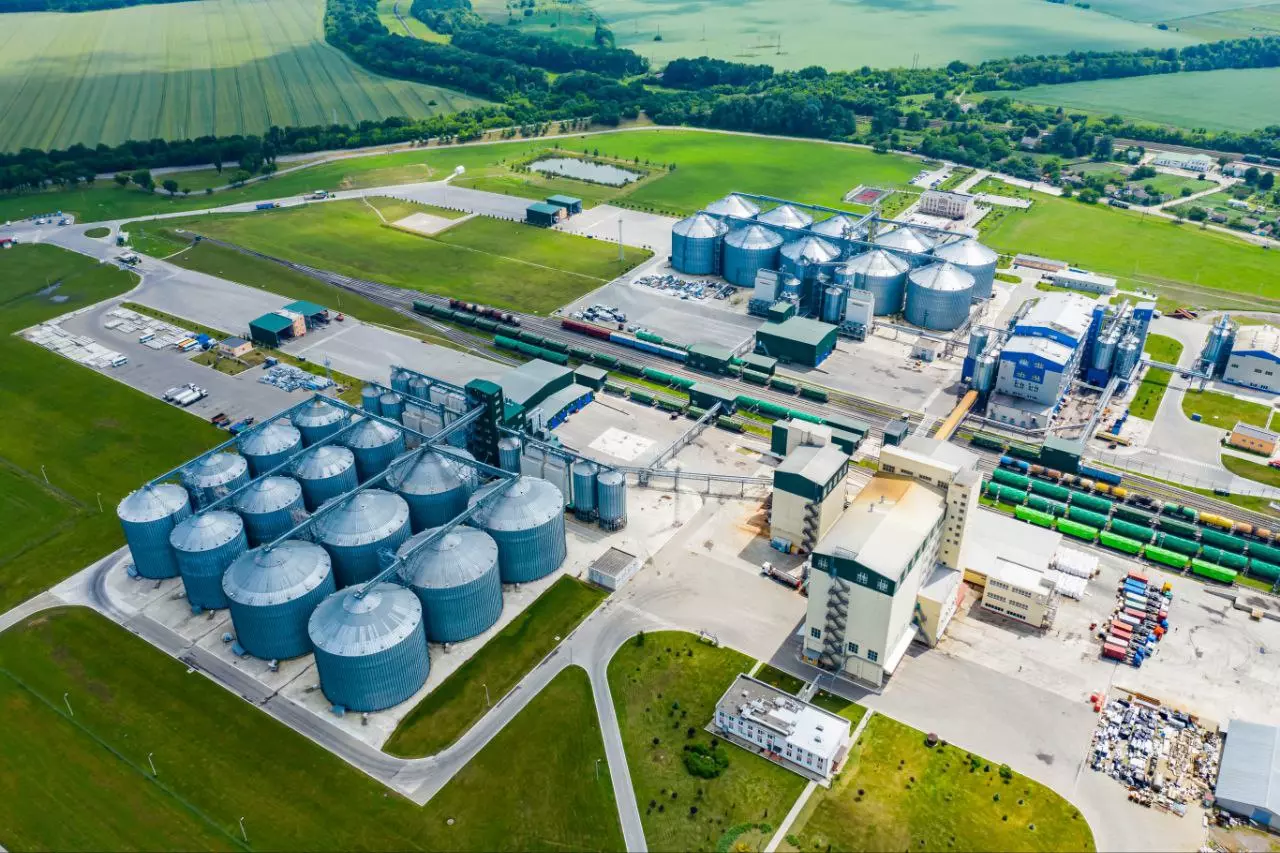
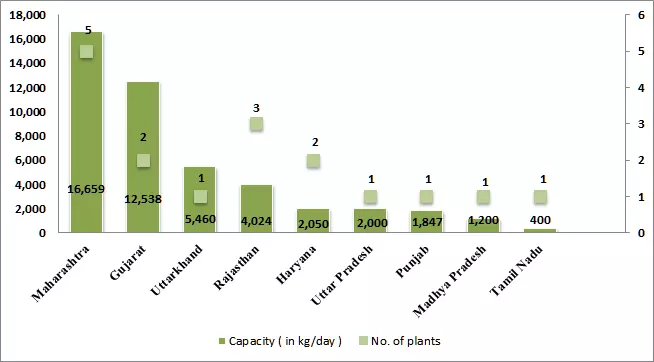
According to the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, as of March 2021, the country has over 200 operational bio-CNG plants with a total production capacity of around 400,000 metric tonnes per annum. Today, the majority of these plants are located in UP and Gujarat.
What is Bio-CNG?
Bio-CNG plants are a type of CNG (compressed natural gas) plant that uses biomass as the feedstock. Biomass is essentially any organic material that can be converted into energy, including agricultural waste, sewage sludge and animal manure. The benefits of using bio-CNG in your vehicle include:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels;
- A renewable source of fuel; and
- The ability to use waste products as an alternative fuel source.
How is Bio-CNG produced?
The process of producing Bio-CNG involves two main steps which are:
2. The second step is the purification of the biogas through a process called upgrading, which removes impurities such as carbon dioxide and moisture, leaving behind pure methane gas.
The purified methane gas is then compressed and stored as Bio-CNG, which can be used as a clean and renewable fuel for transportation, cooking, and heating.
Read this blog also: Bio-CNG: A Stubble Burning Alternative and Lifesaver Of Air
Factors to consider before setting up a Bio-CNG plant
1. Raw Material Availability
- Type of feedstock: The availability and suitability of different types of feedstock should be considered, such as agricultural residues, food waste, and animal waste.
- Quantity and quality: The availability of sufficient quantities of high-quality feedstock should be ensured for sustainable production, as it can possibly cause disruption and affect profitability during shortages.
2. Location
- Proximity to raw material source: The plant should be located near the raw material source to minimize transportation costs and reduce environmental impact. Also, it is advisable that the plant should be situated within a 15-kilometer radius of the readily available biomass as they are not economically viable due to their low energy content per volume and huge quantity.
- Access to infrastructure: The plant should have access to essential infrastructure, such as water, electricity, and gas supply.
- Choice of technology: The technology used for producing Bio-CNG should be chosen based on the feedstock and desired output.
- Efficiency and reliability: The technology should be efficient, reliable, and easy to maintain to ensure the smooth operation of the plant.
- Market demand: The plant’s capacity should be aligned with the market demand for the product to avoid overcapacity or under-capacity issues.
- Scale of operation: The scale of the plant should be considered, which can vary from small-scale to large-scale production.
- Permits and regulations: The plant should comply with the relevant local and national regulations and permits related to environmental, safety, and quality standards.
- Compliance costs: The cost of complying with regulations and permits should be factored into the financial viability of the project.
- Capital investment: The cost of setting up the plant should be carefully assessed, including the cost of land, building, equipment, and labor.
- Operating costs: The plant’s operating costs, including feedstock procurement, production, and maintenance costs, should be analyzed.
- Revenue generation: The revenue generation potential of Bio-CNG, including market demand and pricing, should be evaluated to ensure the plant’s financial viability.
Government’s take on Bio-CNG
Conclusive thoughts
Switch to cleaner fuel today! Discover the leading bio-CNG manufacturer in India and fuel your vehicles sustainably. Join the green revolution and reduce emissions. Contact us now!




